File Upload
Universal upload component for @midwayjs/faas, @midwayjs/web, @midwayjs/koa and @midwayjs/express multiple frameworks, supports file (server temporary file) and stream (stream) two modes.
Related Information:
| web support | |
|---|---|
| @midwayjs/koa | ✅ |
| @midwayjs/faas | 💬 |
| @midwayjs/web | ✅ |
| @midwayjs/express | ✅ |
💬 Some function computing platforms do not support streaming request responses. Please refer to the corresponding platform capabilities.
Install dependencies
$ npm i @midwayjs/upload@3 --save
Or add the following dependencies in package.json and reinstall.
{
"dependencies": {
"@midwayjs/upload": "^3.0.0",
//...
},
"devDependencies": {
//...
}
}
Enable component
import { Configuration } from '@midwayjs/core';
import * as upload from '@midwayjs/upload';
@Configuration({
imports: [
// ...other components
upload
],
//...
})
export class MainConfiguration {}
- Get the uploaded file in the code
import { Controller, Inject, Post, Files, Fields } from '@midwayjs/core';
@Controller('/')
export class HomeController {
@Inject()
ctx;
@Post('/upload')
async upload(@Files() files, @Fields() fields) {
/*
files = [
{
filename: 'test.pdf', // original name of the file
data: '/var/tmp/xxx.pdf', // when the mode is file, it is the server temporary file address
fieldname: 'test1', // form field name
mimeType: 'application/pdf', // mime
},
{
filename: 'test.pdf', // original name of the file
data: ReadStream, // when the mode is stream, it is the server temporary file address
fieldname: 'test2', // form field name
mimeType: 'application/pdf', // mime
},
// ...file supports uploading multiple files at the same time
]
*/
return {
files,
fields
}
}
}
If the swagger component is enabled at the same time, please be sure to add the type of the upload parameter (the type corresponding to the decorator, and the type in @ApiBody), otherwise an error will be reported. For more information, please refer to the file upload section of swagger.
configuration
default allocation
The default configuration is as follows, and generally does not need to be modified.
// src/config/config.default.ts
import { uploadWhiteList } from '@midwayjs/upload';
import { tmpdir } from 'os';
import { join } from 'path';
export default {
//...
upload: {
// mode: UploadMode, the default is file, that is, upload to the temporary directory of the server, and can be configured as stream
mode: 'file',
// fileSize: string, the maximum upload file size, the default is 10mb
fileSize: '10mb',
// whitelist: string[], file extension whitelist
whitelist: uploadWhiteList. filter(ext => ext !== '.pdf'),
// tmpdir: string, temporary storage path for uploaded files
tmpdir: join(tmpdir(), 'midway-upload-files'),
// cleanTimeout: number, how long the uploaded file is automatically deleted in the temporary directory, the default is 5 minutes
cleanTimeout: 5 * 60 * 1000,
// base64: boolean, set whether the original body is in base64 format, the default is false, generally used for compatibility with Tencent Cloud
base64: false,
// Parse the file information in the body only when the matching path reaches /api/upload
match: /\/api\/upload/,
},
}
Upload mode - file
file is the default and recommended by the framework.
Configure upload mode as file string, or use UploadMode.File exported by @midwayjs/upload package.
When using the file mode, the data obtained from this.ctx.files is the temporary file address of the uploaded file on the server, and the content of this file can be obtained later by fs.createReadStream and other methods.
When using the file mode, it supports uploading multiple files at the same time, and multiple files will be stored in this.ctx.files in the form of an array.
When the file mode is adopted, since the upload component will match according to the method of the request and some of the iconic content in headers when receiving the request, if it is considered to be a file upload request, the request will be Parse and write the files in it to the temporary cache directory of the server. You can set the path that allows parsing files through match or ignore configuration of this component.
After configuring match or ignore, you can ensure that your normal post and other request interfaces will not be illegally used by users for uploading, and you can avoid the risk of the server cache being full.
You can check the section Configuring the upload path to allow (match) or ignore (ignore) below to configure it.
Upload mode - stream
Configure upload mode as stream string, or use UploadMode.Stream exported by @midwayjs/upload package to configure.
When using the stream mode, the data obtained from this.ctx.files is ReadStream, and then the data stream can be transferred to other WriteStream or TransformStream through pipe and other methods.
When using stream mode, only one file is uploaded at the same time, that is, there is only one file data object in this.ctx.files array.
In addition, the stream mode will not generate temporary files on the server, so there is no need to manually clear the temporary file cache after getting the uploaded content.
Upload whitelist
Through the whitelist attribute, configure the file extensions that are allowed to be uploaded. If null is configured, the extensions will not be verified.
If the configuration is null, the suffix name of the uploaded file will not be verified. If the file upload mode (mode=file) is adopted, it may be used by attackers to upload .php, .asp and other suffixes The WebShell implements the attack behavior.
Of course, since the @midwayjs/upload component will rerandomly generate the file name of the uploaded temporary file, as long as the developer does not return the address of the uploaded temporary file to the user, then even if the user uploads For some unexpected files, there is no need to worry too much about being used.
If the uploaded file suffix does not match, a 400 error will be responded, and the default values are as follows:
'.jpg',
'.jpeg',
'.png',
'.gif',
'.bmp',
'.wbmp',
'.webp',
'.tif',
'.psd',
'.svg',
'.js',
'.jsx',
'.json',
'.css',
'.less',
'.html',
'.htm',
'.xml',
'.pdf',
'.zip',
'.gz',
'.tgz',
'.gzip',
'.mp3',
'.mp4',
'.avi',
The default suffix whitelist can be obtained through the uploadWhiteList exported in the @midwayjs/upload package.
In addition, midway upload component, in order to avoid some malicious users, uses some technical means to forge some extensions that can be truncated, so it will filter the binary data of the obtained extensions, and only support 0x2e (that is, the English dot .), 0x30-0x39 (that is, the number 0-9), 0x61-0x7a (that is, the lowercase letters a-z) are used as extensions, and other characters will be Automatically ignored.
Starting with v3.14.0, you can pass a function that can dynamically return a whitelist based on different conditions.
// src/config/config.default.ts
import { uploadWhiteList } from '@midwayjs/upload';
import { tmpdir } from 'os';
import { join } from 'path';
export default {
// ...
upload: {
whitelist: (ctx) => {
if (ctx.path === '/') {
return [
'.jpg',
'.jpeg',
];
} else {
return [
'.jpg',
]
};
},
// ...
},
}
MIME type checking
Some malicious users will try to modify the extension of .php and other WebShells to .jpg to bypass the whitelist filtering rules based on the extension. In some server environments, this jpg file will still be used as PHP scripts to execute, pose a security risk.
Therefore, the @midwayjs/upload component provides the mimeTypeWhiteList configuration parameter 【Please note that this parameter has no default value setting, that is, no verification by default】, you can set the allowed file MIME format through this configuration, A rule is a secondary array consisting of an array [extension, mime, [...moreMime]], for example:
// src/config/config.default.ts
import { uploadWhiteList } from '@midwayjs/upload';
export default {
//...
upload: {
//...
// extension whitelist
whitelist: uploadWhiteList,
// Only the following file types are allowed to be uploaded
mimeTypeWhiteList: {
'.jpg': 'image/jpeg',
// Multiple MIME types can also be set, for example, the following files that allow the .jpeg suffix are jpg or png
'.jpeg': ['image/jpeg', 'image/png'],
// other types
'.gif': 'image/gif',
'.bmp': 'image/bmp',
'.wbmp': 'image/vnd.wap.wbmp',
'.webp': 'image/webp',
}
},
}
You can also use the DefaultUploadFileMimeType variable provided by the @midwayjs/upload component as the default MIME validation rule, which provides commonly used .jpg, .png, .psd and other file extensions MIME data:
// src/config/config.default.ts
import { uploadWhiteList, DefaultUploadFileMimeType } from '@midwayjs/upload';
export default {
//...
upload: {
//...
// extension whitelist
whitelist: uploadWhiteList,
// Only the following file types are allowed to be uploaded
mimeTypeWhiteList: DefaultUploadFileMimeType,
},
}
You can query the file format and corresponding MIME mapping through https://mimetype.io/. For the MIME identification of files, we use [file-type@16](https://www. npmjs.com/package/file-type) this npm package, please note the file types it supports.
The MIME type verification rule is only applicable to the file upload mode mode=file, and after setting this verification rule, since the file content needs to be read for matching, the upload performance will be slightly affected.
However, we still recommend that you set the mimeTypeWhiteList parameter if possible, which will improve your application security.
Starting with v3.14.0, you can pass a function that dynamically returns MIME rules based on different conditions.
// src/config/config.default.ts
import { tmpdir } from 'os';
import { join } from 'path';
export default {
// ...
upload: {
mimeTypeWhiteList: (ctx) => {
if (ctx.path === '/') {
return {
'.jpg': 'image/jpeg',
};
} else {
return {
'.jpeg': ['image/jpeg', 'image/png'],
}
};
}
},
}
Configure match or ignore
When the upload component is enabled, when the method of the request is one of POST/PUT/DELETE/PATCH, if it is judged that headers['content-type'] of the request contains multipart/form-data and When boundary is set, it will **automatically enter** upload file parsing logic.
This will cause: If the user may manually analyze the request information of the website, manually call any interface such as post, and upload a file, it will trigger the parsing logic of the upload component, and create a file in the temporary directory The temporary cache of uploaded files will generate unnecessary load on the website server, and may affect the normal business logic processing of the server in severe cases.
Therefore, you can add match or ignore configuration to the configuration to set which api paths are allowed to upload.
Same name Field
The componennt support Field with the same name since v3.16.6.
// src/config/config.default.ts
import { tmpdir } from 'os';
import { join } from 'path';
export default {
// ...
upload: {
allowFieldsDuplication: true
},
}
After allowFieldsDuplication is enabled, Fields with the same name will be merged into an array.
import { Controller, Inject, Post, Files, Fields } from '@midwayjs/core';
@Controller('/')
export class HomeController {
@Post('/upload')
async upload(@Files() files, @Fields() fields) {
/*
fields = {
name: ['name1', 'name2'],
otherName: 'nameOther'
// ...
}
*/
}
}
Temporary files and cleanup
If you use the file mode to get uploaded files, the uploaded files will be stored in the folder pointed to by the tmpdir option in the configuration of the upload component that you set in the config file.
You can control the automatic temporary file cleanup time by using cleanTimeout in the configuration, the default value is 5 * 60 * 1000, that is, the uploaded file will be automatically cleaned up after 5 minutes, set it to 0 To disable the automatic cleaning function.
You can also actively clean up the temporary files uploaded by the current request by calling await ctx.cleanupRequestFiles() in the code.
Safety warning
- Please pay attention to whether to enable
extension whitelist(whiteList), if the extension whitelist is set tonull, it may be used by attackers to upload.php,.aspand other WebShells. - Please pay attention to whether to set
matchorignorerules, otherwise commonPOST/PUTand other interfaces may be exploited by attackers, resulting in increased server load and large space occupation. - Please pay attention to whether to set the
file type rule(fileTypeWhiteList), otherwise the attacker may forge the file type to upload.
Front-end file upload example
1. The form of html form
<form action="/api/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Name: <input type="text" name="name" /><br />
File: <input type="file" name="testFile" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
2. Fetch FormData method
const fileInput = document. querySelector('#your-file-input');
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', fileInput.files[0]);
fetch('/api/upload', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData,
});
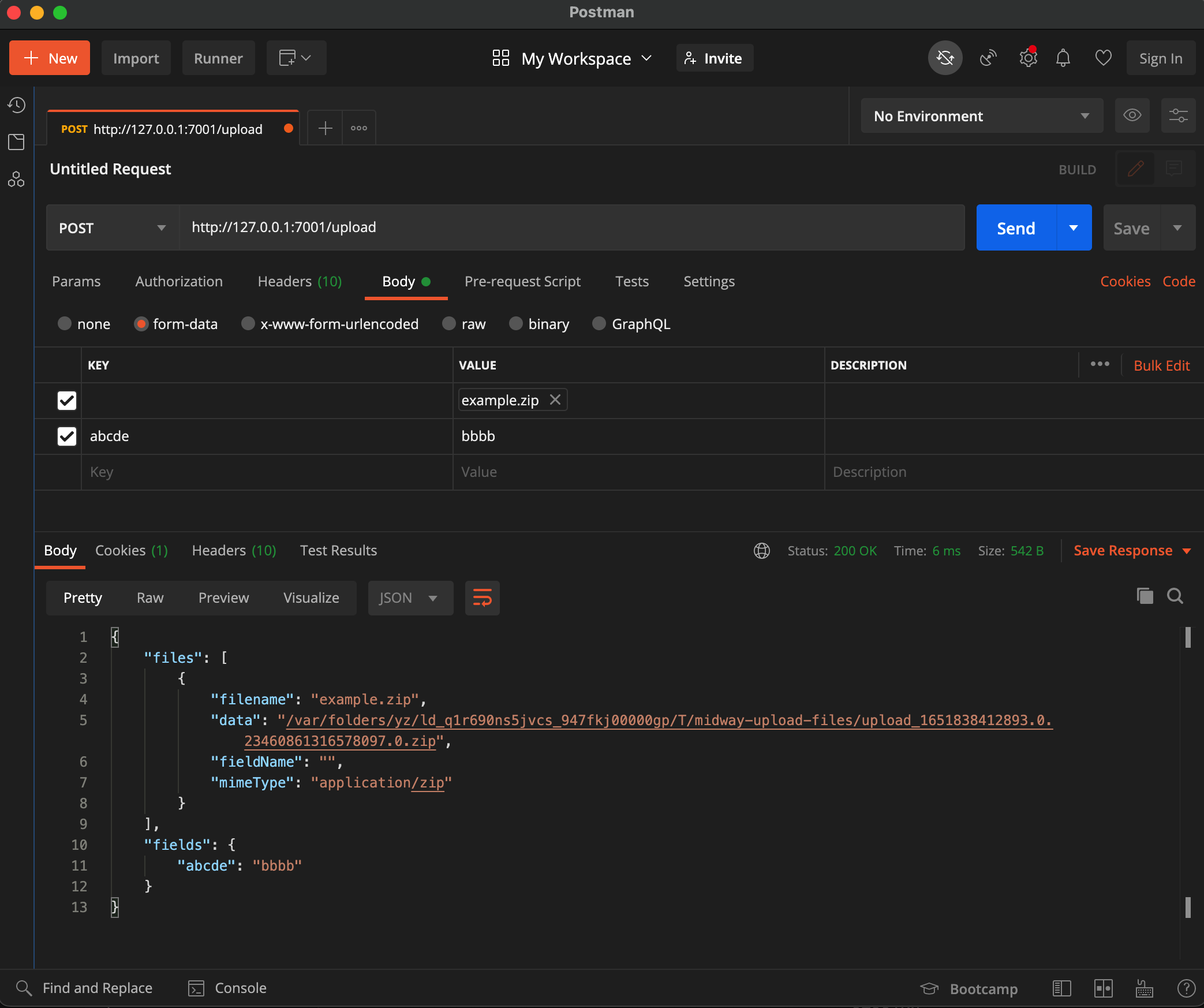
Postman test example